
Lecture 13 Preview Mitosis, Science images, Chromosome
In summary, while chromatin and chromatid are intimately related in the context of chromosomes, they serve different purposes. Chromatin provides a mechanism to package and regulate DNA within the nucleus, and chromatids are pivotal for accurate genetic material distribution during cell division. Aimie Carlson Oct 06, 2023 Comparison Chart

Difference between chromosome and chromatid LORECENTRAL
Definition Chromatin : Chromatin is a DNA and protein complex found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, and plays a major role in DNA packaging mechanisms. Chromatid : Chromatid is a duplicated half of a replicated chromosome, generally appearing during the cell division process.

Diferencia Entre La Cromatina Y Los Cromosomas Dinami
Chromatin is essentially a combination of DNA and protein molecules, forming the structural basis of a chromosome. On the other hand, a chromatid refers to the duplicated, identical form of a chromosome that appears during the cell division process. While chromatin serves as the raw material for chromosomes, chromatids are specific formations.

Chromosomes Vs. Chromatids Chromosome, Science biology, Biology
Difference Between Chromatid And Chromatin In Tabular Form Summary Chromatin is a complex of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and protein found in the eukaryotic cell nucleus whose primary function is packaging very long DNA molecules into a more compact, denser shape, which prevents the strands from becoming tangled. .

chromosomes chromatin Google Search Molecular biology, Teaching biology, Human body systems
As a result, chromatin can be packaged into a much smaller volume than DNA alone. Histones are a family of small, positively charged proteins termed H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 (Van Holde, 1988). DNA.
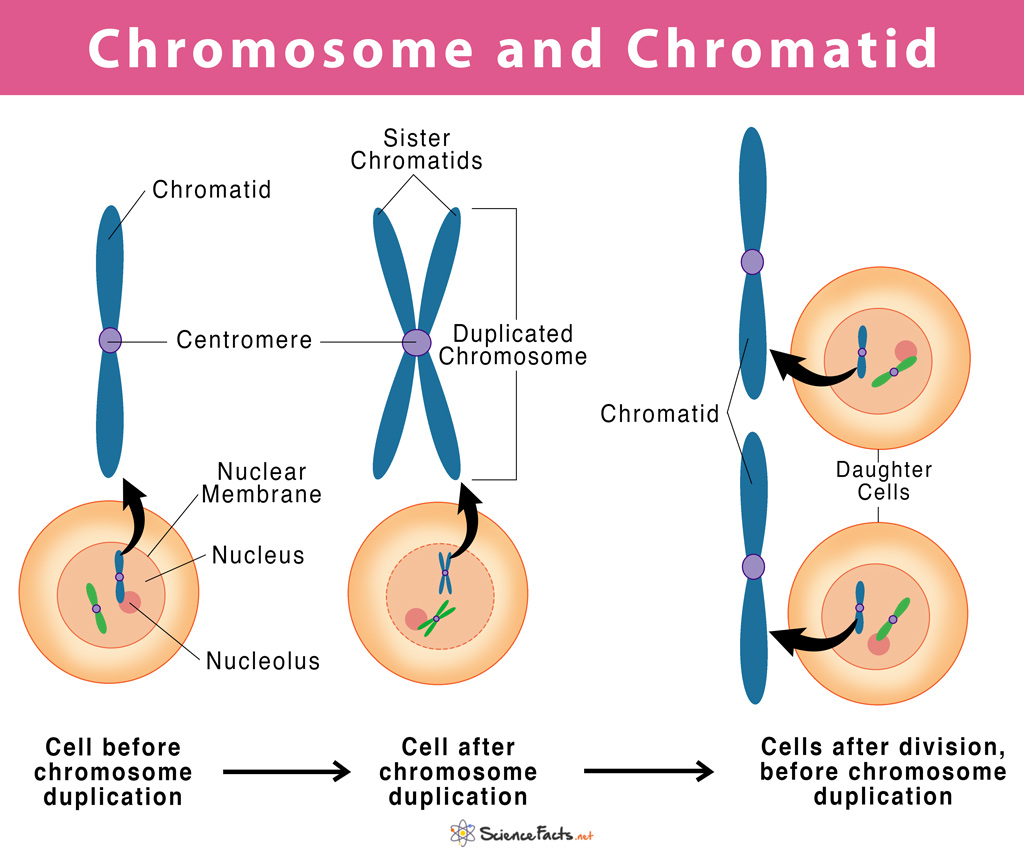
Chromosome vs Chromatid
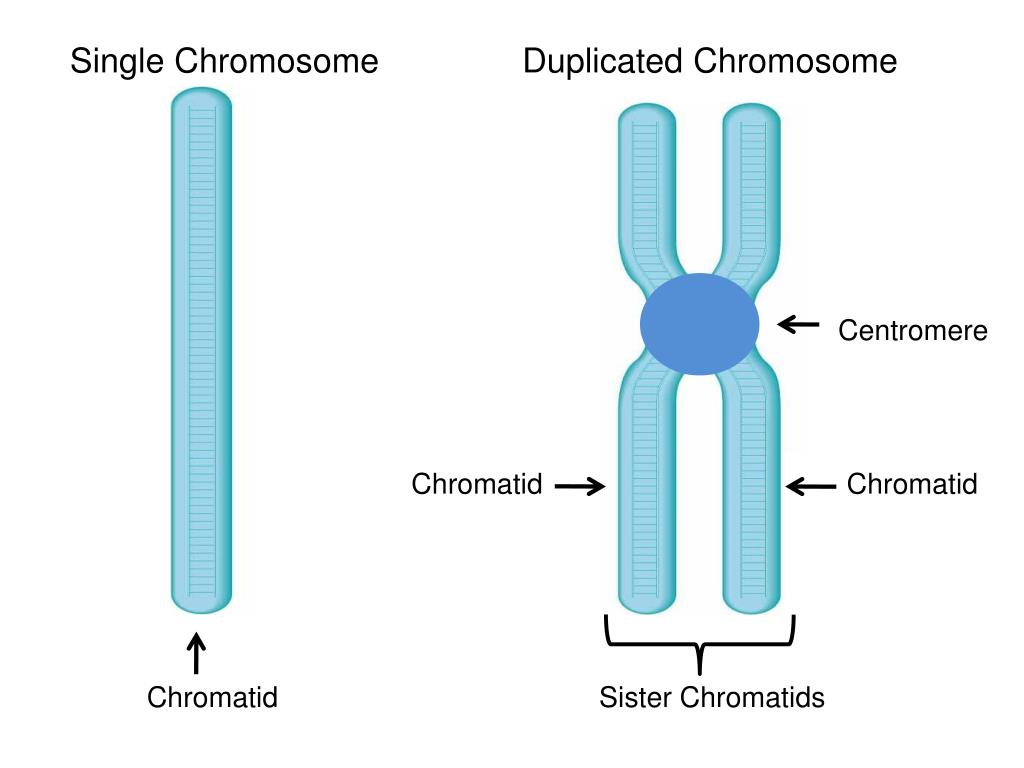
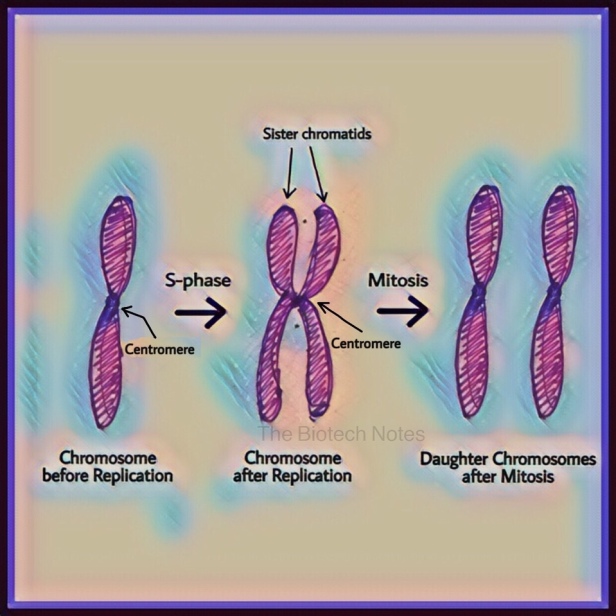
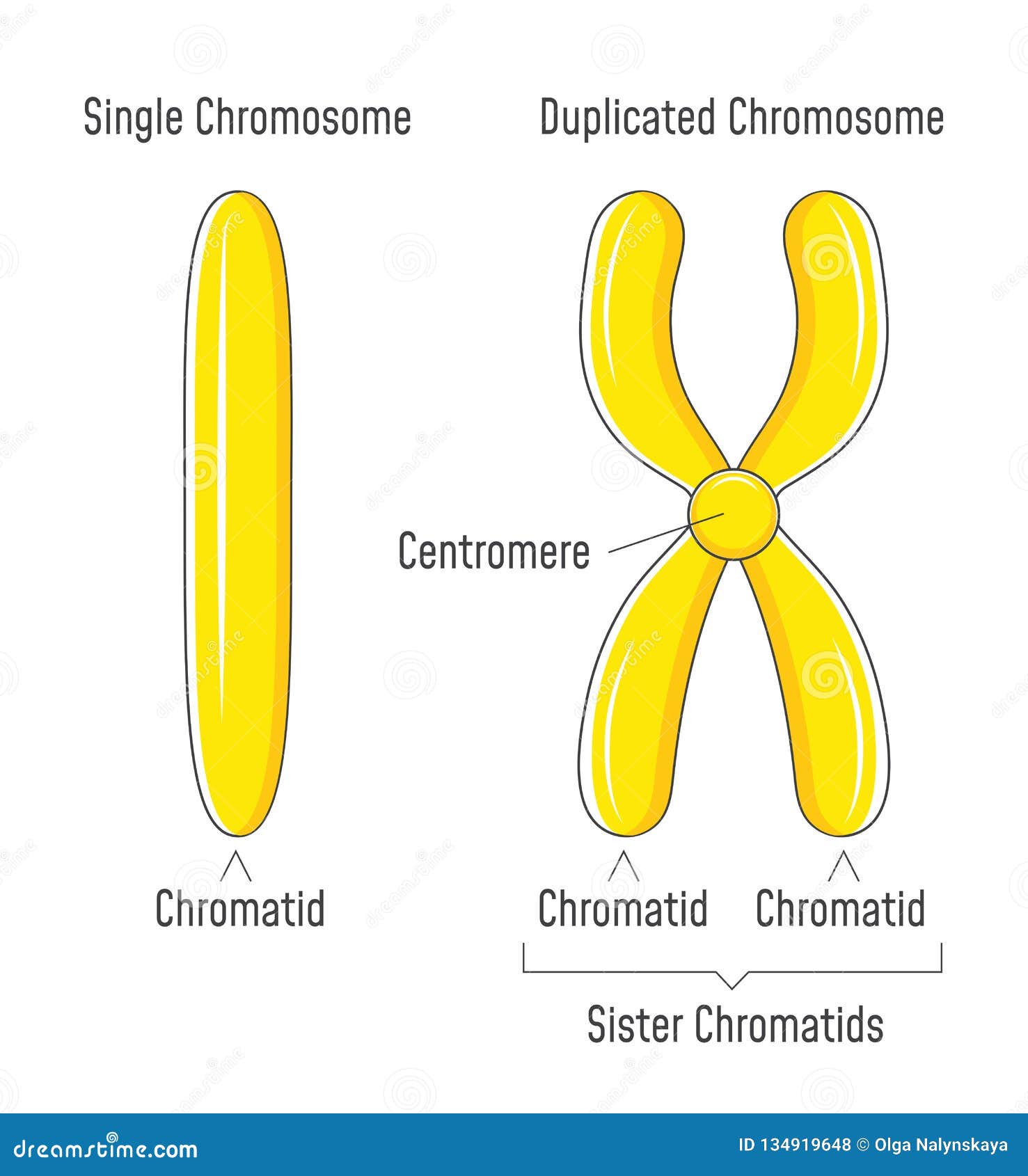
Figure 8.4.3 8.4. 3: Diagram of Replicated and Condensed Eukaryotic Chromosome (sister chromatids). (1) Chromatid - one of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase. (2) Centromere - the point where the two chromatids are joined together. (3) Short arm is termed p; Long arm is termed q.

Differences Between Chromosome and Chromatid Education
Biology definition: Chromatin is a substance made up of DNA or RNA and proteins, such as histones. It condenses during cell division ( mitosis or meiosis) and becomes a chromosome. Chromatins are "unwound" condensed structures whereas chromosomes are highly packaged and more condensed than chromatins.
Eukaryotic Chromosome Structure Chromatin Chromatid Dna
Chromosomes and chromatids are thread-shaped structures in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells (cells consisting of a nucleus within a membrane). They consist of extremely long strands of DNA material which are carriers of genes and regulatory elements. Let us have a closer look at what is what. What are chromosomes?

Chromosome Definition, Structure, Types and Function Biology Ideas
noun the readily stainable substance of a cell nucleus, consisting of DNA, RNA, and various proteins, that forms chromosomes during cell division. chromatid [ kroh-m uh-tid ] show ipa noun one of two identical chromosomal strands into which a chromosome splits longitudinally preparatory to cell division. Compare More Words
Chromatin vs. Chromatid 5 Key Differences, Pros & Cons, Similarities Difference 101
Definition A chromatid is one of the two identical halves of a chromosome that has been replicated in preparation for cell division. The two "sister" chromatids are joined at a constricted region of the chromosome called the centromere. During cell division, spindle fibers attach to the centromere and pull each of the sister.
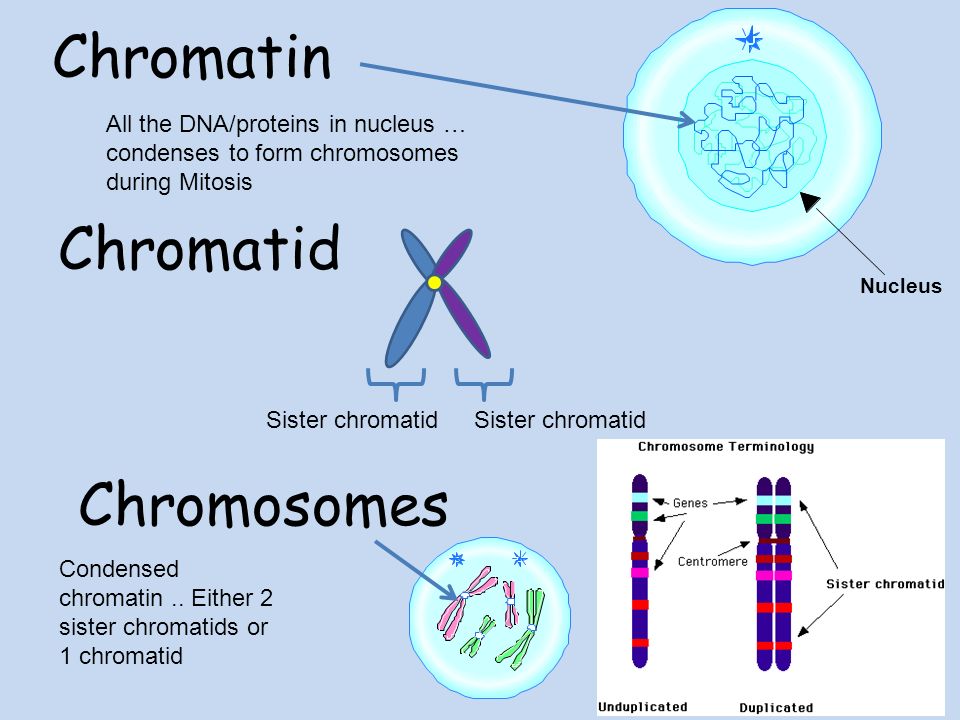
Cells and Inheritance San Francisco de Paula, Science Department.
CHROMATIN is the "Noodle-like" structure present in the nucleus of a cell in Non division state. Whereas, when chromosomes form copies of themselves in order to divide equally among daughter.
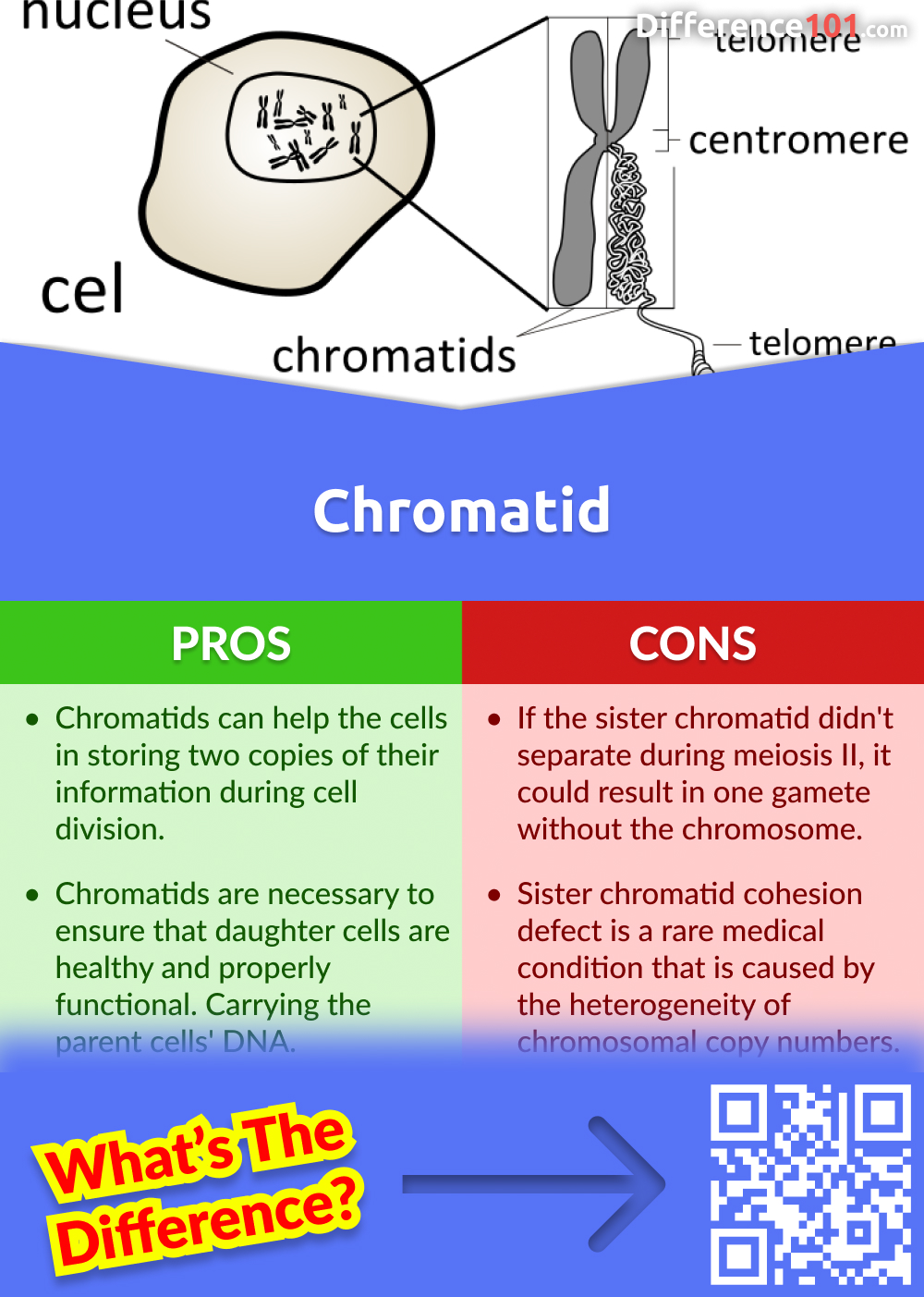
Chromatin vs. Chromatid 5 Key Differences, Pros & Cons, Similarities Difference 101
Chromatin Packaging Varies Within a Chromosome: Euchromatin & Heterochromatin. Classically, there are two major types of chromatin, but these are more the ends of a continuous and varied spectrum. Euchromatin is more loosely packed, and tends to contain genes that are being transcribed (or actively being utilized by the cell). For example.
PPT Cell Division PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2474917
The complex of DNA plus histones and other structural proteins is called chromatin. For most of the life of the cell, chromatin is decondensed, meaning that it exists in long, thin strings that look like squiggles under the microscope.
Chromosomes, Chromatids and chromatin The Biotech Notes
Not only are the genomes of most eukaryotes much more complex than those of prokaryotes, but the DNA of eukaryotic cells is also organized differently from that of prokaryotic cells. The genomes of prokaryotes are contained in single chromosomes, which are usually circular DNA molecules.
Unduplicated and Duplicated Chromosomes. Sister Chromatids Stock Vector Illustration of
Chromatin refers to a mixture of DNA and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms. Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of DNA in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus. Narration 00:00. Chromatin.
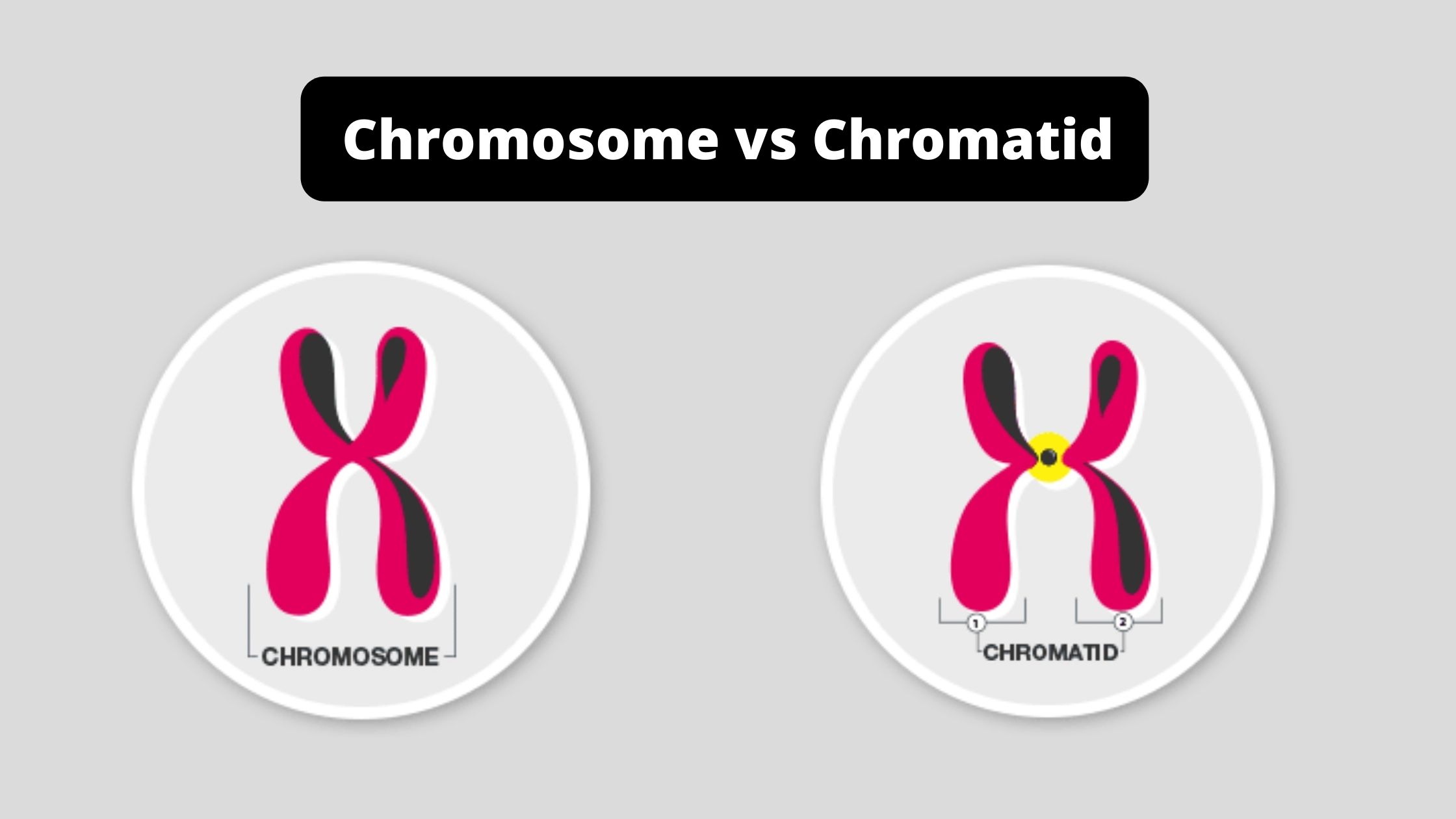
Difference between Chromosome and Chromatid Chromosome vs Chromatid
Introduction to cell division © 2024 Khan Academy Cookie Notice Chromosomes, chromatids and chromatin Google Classroom About Transcript DNA replication, transcription, and translation are key biological processes. Replication involves DNA duplicating itself. Transcription involves DNA creating mRNA, and translation converts mRNA into proteins.